Role of Blockchain in Energy and Finance
Digital Transformation ?? Comments 18/Nov/2025 TueBlockchain technology is transforming energy and financial systems by providing secure, transparent, and decentralized solutions. Its ability to facilitate peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading and ensure transparency in renewable energy certificates (RECs) makes it a valuable tool for advancing sustainability goals. Blockchain’s unique attributes—such as immutability, traceability, and decentralized validation—are particularly well-suited to addressing challenges in energy management and green finance.
Details
-
Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Blockchain technology enables decentralized energy markets where individuals and organizations can trade excess energy directly with one another.
o How It Works:
• Households or businesses with renewable energy systems (e.g., solar panels) generate excess energy that is stored in a local blockchain-powered microgrid.
• Blockchain records every transaction, ensuring that energy production and consumption are tracked securely and transparently.
• Smart contracts—automated agreements encoded on the blockchain—facilitate real-time energy trading by matching buyers and sellers based on supply, demand, and pricing.
o Benefits:
• Reduces reliance on centralized energy utilities by empowering local communities.
• Encourages the adoption of renewable energy by creating financial incentives for producing surplus energy.
• Enhances energy resilience by enabling localized energy sharing during outages or peak demand periods.
-
Transparent Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) Blockchain technology ensures the authenticity and traceability of renewable energy certificates, which verify that energy has been generated from renewable sources.
o How It Works:
• When renewable energy is produced, a corresponding REC is issued on a blockchain ledger, recording key details such as the source, location, and time of generation.
• Buyers of RECs—such as businesses seeking to meet sustainability targets—can verify the certificate’s authenticity and trace its origin in real-time.
o Benefits:
• Reduces fraud and double-counting in the REC market by creating a tamper-proof record of ownership.
• Enhances trust and transparency for buyers and sellers, encouraging greater participation in renewable energy markets.
• Streamlines administrative processes, reducing costs and improving efficiency in REC issuance and trading.
-
Decentralized Financing for Renewable Energy Projects Blockchain also enables innovative financing models, such as tokenized investments in renewable energy projects.
o How It Works:
• Investors purchase blockchain tokens representing a share in a renewable energy project, such as a wind farm or solar installation.
• The blockchain ensures secure and transparent management of funds, while smart contracts automate dividend payments based on project performance.
o Benefits:
• Lowers barriers to entry for small-scale investors.
• Increases transparency in project funding and revenue distribution.
Practical Example
Blockchain-Powered Microgrid for Neighborhood Energy Sharing
• Scenario: A neighborhood installs solar panels on several homes, creating a surplus of renewable energy that exceeds the local demand at certain times of the day.
• Solution: A blockchain-powered microgrid is implemented to facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading among residents.
o Residents with excess solar energy sell it to their neighbors at a competitive rate, tracked and validated by the blockchain.
o Smart contracts automate payments and energy transfers, ensuring a seamless and trustless trading experience.
o Each transaction is recorded immutably on the blockchain, allowing participants to view their energy contributions and consumption transparently.
• Outcome:
o The neighborhood reduces its reliance on external utilities, lowering energy costs.
o Residents who generate surplus energy earn additional income, incentivizing further investment in solar panels.
o The system enhances energy resilience, ensuring consistent energy access during outages.
Applications of Blockchain in Green Finance and Energy
-
Distributed Renewable Energy Markets: Blockchain facilitates decentralized energy markets, enabling efficient energy sharing across communities, campuses, and businesses.
-
Green Bonds and Carbon Credits: Blockchain platforms simplify the issuance, tracking, and trading of green bonds and carbon credits, ensuring transparency and accountability.
-
Supply Chain Traceability: Blockchain tracks renewable energy and green products throughout the supply chain, ensuring that sustainability claims are verified and trustworthy.
-
Incentive Programs: Blockchain-based rewards systems encourage sustainable behaviors, such as recycling or energy conservation, by issuing tokens or credits redeemable for goods or services.
Key Benefits of Blockchain in Energy and Finance
-
Transparency: Blockchain provides a tamper-proof record of transactions, ensuring trust and accountability in energy markets and green finance.
-
Efficiency: Smart contracts automate processes such as energy trading, REC issuance, and financing, reducing administrative overhead and costs.
-
Decentralization: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain empowers individuals and communities to participate directly in energy markets and project financing.
-
Scalability: Blockchain systems can accommodate growing numbers of participants and transactions, making them suitable for large-scale applications.
-
Incentivization of Sustainability: Blockchain enables innovative models that reward individuals and businesses for adopting renewable energy and sustainable practices.
By leveraging blockchain technology, individuals, communities, and businesses can unlock new opportunities in renewable energy adoption and green finance, fostering a more sustainable and decentralized energy future.
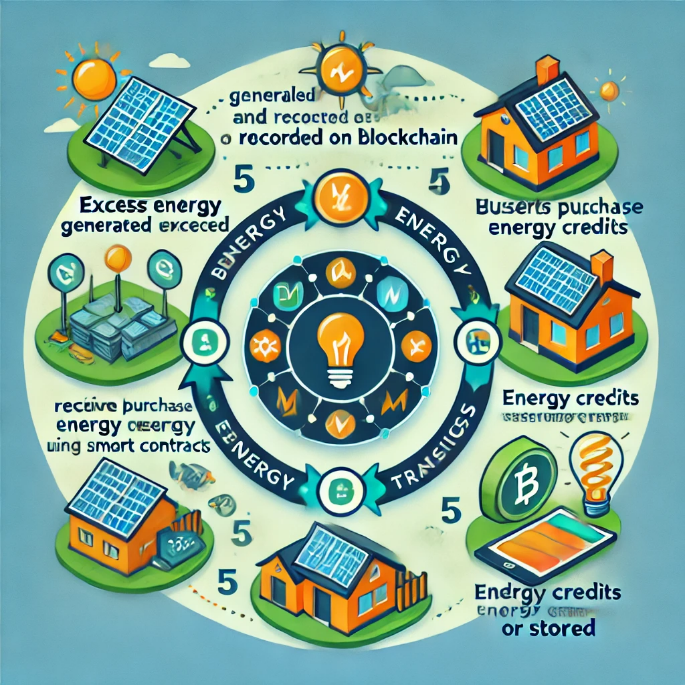
• Diagram showing blockchain-enabled energy transactions within a community.
o Excess energy generated by solar panels is recorded on the blockchain.
o Blockchain verifies and tracks energy transfers between households.
o Users purchase energy credits securely using smart contracts.
o Households receive updates on their energy usage and savings.
o Energy credits can be traded within the community or stored for future use.
Tags: energy sustainability blockchain finance